Home
Services
Reconstructive Surgery
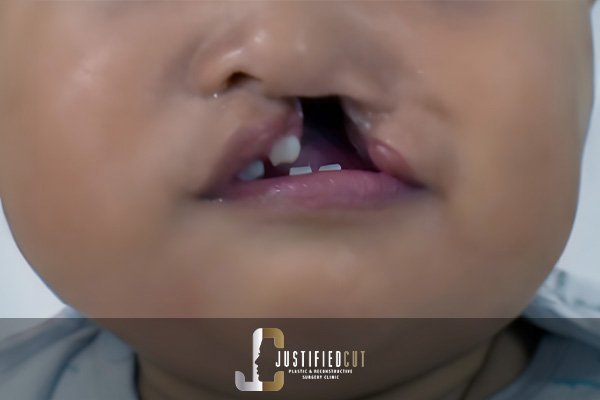
Congenital Anomalies
Acute Burn
Burn Complications and Contractures
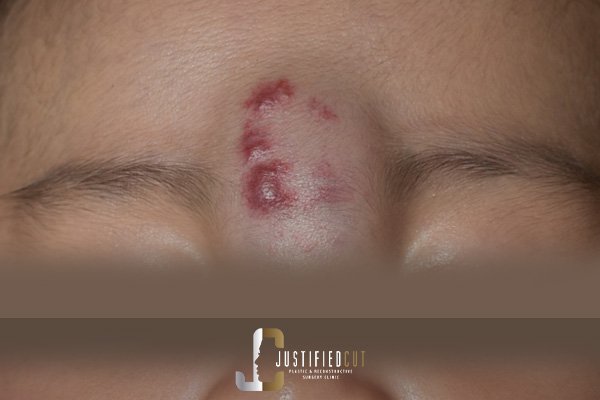
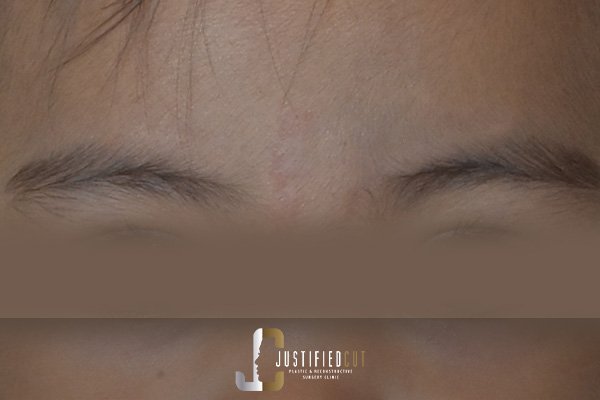
Facial Lacerations, Avulsion, Injuries, Fractures, Facial Masses / Tumors
Face, Scalp, Trunk, Breast, Abdominal Wall (hernia) and Extremity Reconstruction (Grafting and Flaps)
Genitalia (Circumcision)
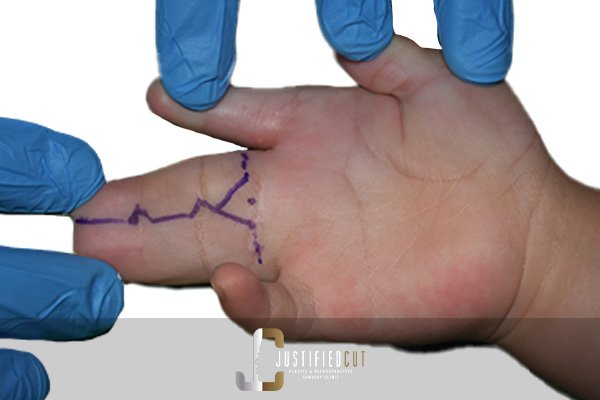
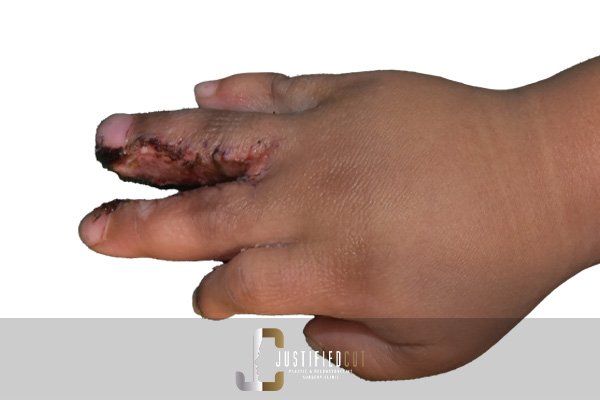
Hand Injuries
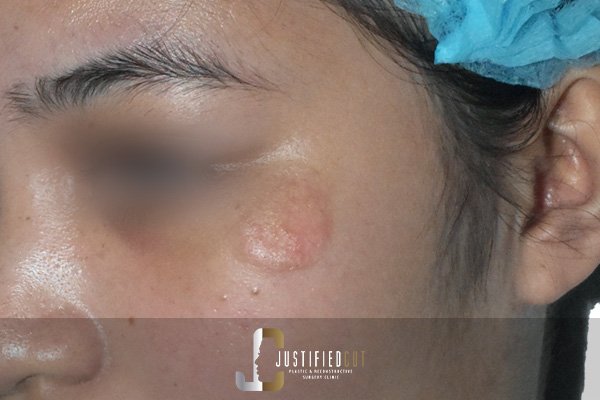
Skin Lesions / Skin Cancers
Scar Revision and Management
Wound Care For Simple and Complicated Wounds
Non-Surgical Aesthetic Treatments
Justified Cut
Location
Contact Us
+63 999 854 8889
+63 945 123 8818
5.0 Average Rating